|
This section details the various connection settings available for performing queries on Microsoft SQL database server. First steps are common to all database queries and connection methods. They are documented in the Database Query Analysis section.
Step 5.1a - Setting Command line connection to Microsoft SQL database servers
If you have selected Command Line Utility as the connection method, the following panel is displayed:
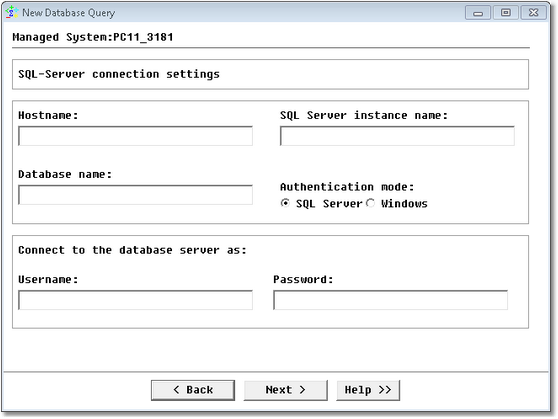
Database Query Analysis Wizard — Microsoft SQL Server Command Line Connection Settings
| • | Hostname: Name of the server where SQL Server is running (hostname or IP address) |
| • | SQL Server instance name: Specify the SQL server instance name if there are several SQL Server instances installed. Leave "default" if there is a single instance |
| • | Database name: Name of the database |
| • | Authentication mode (SQL Server/Windows): Select Windows if you wish to connect to the database through a Windows user account. Select SQL Server if you wish to connect to the database with a specified login name and password from a non-trusted connection. In that case, SQL Server performs the authentication itself by checking if a SQL Server login account has been set up and if the specified password matches the one previously recorded. If SQL Server does not have a login account set, authentication fails and you get an error message. Please note that since version 8.6.54, SSL encryption is supported |
| • | Username: Account used to connect to the database |
| • | Password: Password associated with the specified username |
Click Next to access the query definition panel.
Step 5.2a - Setting JDBC connection to Microsoft SQL database servers
If you have selected Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) as the connection method, the following panel is displayed:
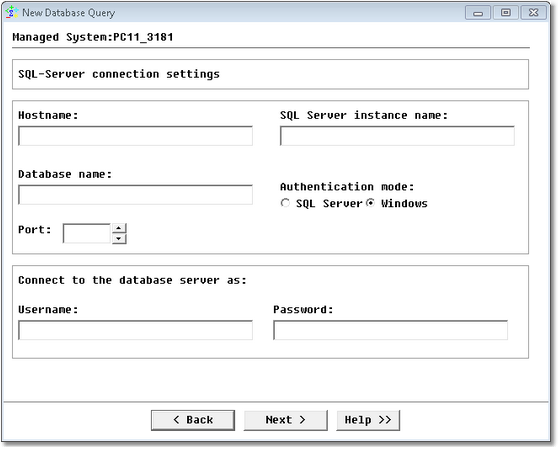
Database Query Analysis Wizard — MS SQL Server JDBC Connection Settings
| • | Hostname: Name of the server where SQL Server is running (hostname or IP address) |
| • | SQL Server instance name: Specify the SQL server instance name if there are several SQL Server instances installed. Leave "default" if there is a single instance |
| • | Database name: Name of the database |
| • | Authentication mode (SQL Server/Windows): Select Windows if you wish to connect to the database through your Windows user account. Select SQL Server if you wish to connect to the database with a specified login name and password from a non-trusted connection. In that case, SQL Server performs the authentication itself by checking if a SQL Server login account has been set up and if the specified password matches the one previously recorded. If SQL Server does not have a login account set, authentication fails and you get an error message. |
| • | Port: Specify the Microsoft SQL port number |
| • | Username: Account used to connect to the database |
| • | Password: Password associated with the specified username |
Click Next to access the query definition panel
Step 5.3a - Setting ODBC connection to Microsoft SQL database servers
If you have selected Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) as the connection method, the following panel is displayed:
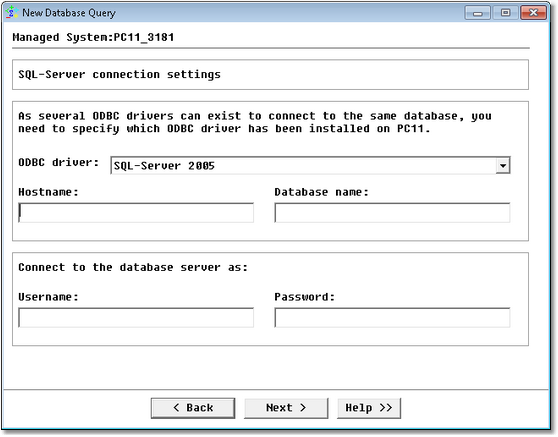
Database Query Analysis Wizard — MS SQL Server ODBC Connection Settings
| • | ODBC Driver: Select the appropriate ODBC driver. The ODBC driver must be installed on the PATROL Agent |
| • | Hostname: Name of the server where SQL Server is running (hostname or IP address) |
| • | Database name: Name of the database |
| • | Username: SQL Server account used to connect to the database |
| • | Password: Password associated with the specified username |
 Monitoring Studio supports two drivers for Windows: SQL Server and SQL Server 2005; and one driver for UNIX: Easysoft ODBC-SQL Monitoring Studio supports two drivers for Windows: SQL Server and SQL Server 2005; and one driver for UNIX: Easysoft ODBC-SQL
Click Next to access the query definition panel.
|