|
This section details the various connection settings available for performing queries on MySQL database server. First steps are common to all database queries and connection methods. They are documented in the Database Query Analysis section.
Step 5.1b - Setting Command line connection for MySQL database servers
If you have selected Command Line Utility as the connection method, the following panel is displayed:
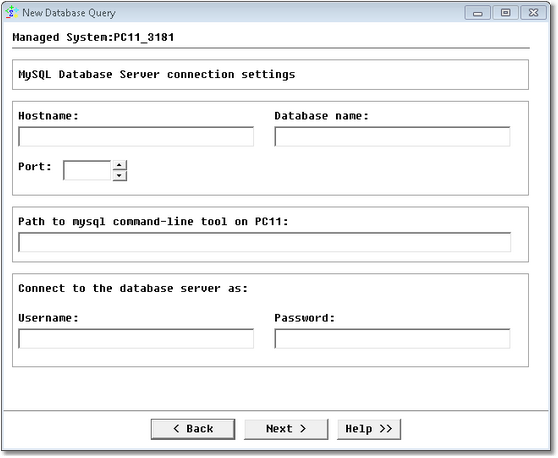
Database Query Analysis Wizard — MySQL Database Server Command Line Connection Settings
| • | Hostname: Name of the server where MySQL Server is running (hostname or IP address) |
| • | Database name: Name of the database |
| • | Port: Specify the MySQL port number |
| • | Path to mysql command-line tool: Enter the path to the mysql tool |
| • | Username: MySQL Server account used to connect to the database |
| • | Password: Password associated with the specified username |
Click Next to access the query definition panel.
 Monitoring Studio connects to MySQL databases using the mysql command-line tool. This client can be downloaded from the MySQL website and is installed by default when installing a MySQL database. This command-line tool, called mysql on Linux/UNIX and mysql.exe on Windows needs to be installed on the system that will perform the SQL queries. Monitoring Studio uses the following optional mysql parameters to connect to the database and execute the SQL query: Monitoring Studio connects to MySQL databases using the mysql command-line tool. This client can be downloaded from the MySQL website and is installed by default when installing a MySQL database. This command-line tool, called mysql on Linux/UNIX and mysql.exe on Windows needs to be installed on the system that will perform the SQL queries. Monitoring Studio uses the following optional mysql parameters to connect to the database and execute the SQL query:
connect_timeout: The number of seconds before connection timeout (as entered in the Monitoring Studio interface).
| ✓ | quick: Do not cache each query result; print each row as it is received. This may slow down the server if the output is suspended. With this option, mysql does not use the history file. It forces mysql to retrieve results from the server a row at a time rather than retrieving the entire result set and buffering it in memory before displaying it. This is done to avoid problems due to insufficient memory for large result sets. |
| ✓ | safe_updates: Allow only those UPDATE and DELETE statements that specify which rows to modify by using key values. |
| ✓ | silent: Silent mode. Produce less output. |
| ✓ | skip_column_names: Do not write column names in results. |
Step 5.2b - Setting JDBC connection to MySQL database servers
If you have selected Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) as the connection method, the following panel is displayed:
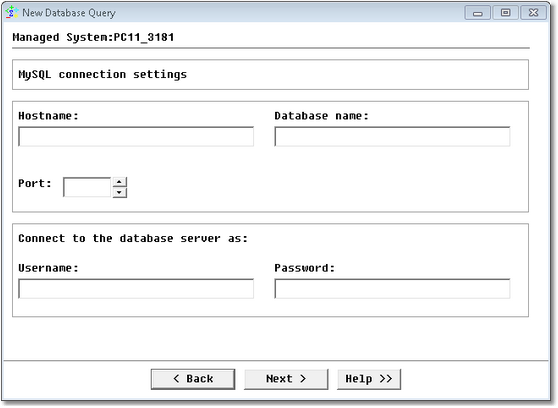
Database Query Analysis Wizard — MySQL Database Server JDBC Connection Settings
| • | Hostname: Name of the server where MySQL Server is running (hostname or IP address) |
| • | Database name: Name of the database |
| • | Port: Specify the MySQL port number |
| • | Username: Account used to connect to the database |
| • | Password: Password associated with the specified username |
Click Next to access the query definition panel.
Step 5.3b - Setting ODBC connection to MySQL database servers
If you have selected Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) as the connection method, the following panel is displayed:
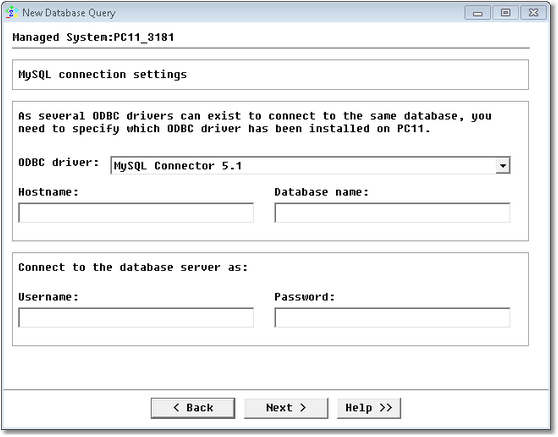
Database Query Analysis Wizard — MySQL Database Server ODBC Connection Settings
| • | ODBC Driver (for ODBC Connection only): Select the appropriate ODBC driver. The ODBC driver must be installed on the PATROL Agent |
| • | Hostname: Name of the server where MySQL Server is running (hostname or IP address) |
| • | Database name: Name of the database |
| • | Username: Account used to connect to the database |
| • | Password: Password associated with the specified username |
 Monitoring Studio provides two drivers (Windows and UNIX): MySQL Connector 3.5 and MySQL Connector 3.51. Monitoring Studio provides two drivers (Windows and UNIX): MySQL Connector 3.5 and MySQL Connector 3.51.
Click Next to access the query definition panel.
|