|
Because String Search, Numeric Value Extractions and Value Map operations cannot always be performed from the raw result output of instances, you may need to first process the multi-line, XML, JSON, or HTML content by using the Text Pre-Processing tool. This tool transforms the result output to simpler format that can be easily parsed with the String Search, Numeric Values Extraction, and Value Map tools.
Example of converting multi-line records to single lines
The "ipconfig /all" command under Windows reports various information about each network card, and each "paragraph" is about one network card:
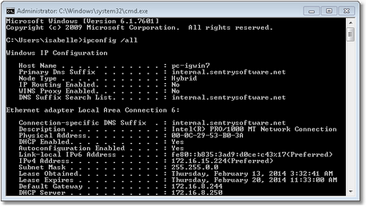
The aim here is to detect any disconnected card. So we add a monitoring instance for the command ipconfig/all. But as the text is in paragraphs, a direct String Search will not get the desired result in this case – which is why we run the Text Pre-Processing tool to convert the multi-line text to single lines.
In the screenshot below, the "ipconfig / all" command is executed and its output is pre-processed to transform its paragraphs into single lines, which in turn enables an efficient parsing with a String Search that looks for "disconnected" network cards.
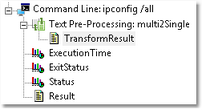
|
To convert multi-line records into single line:
| 1. | In the PATROL Console, right-click the Monitor icon (File, Command Line, Web Request, etc.) and select KM Commands > New > Text Pre-Processing... |
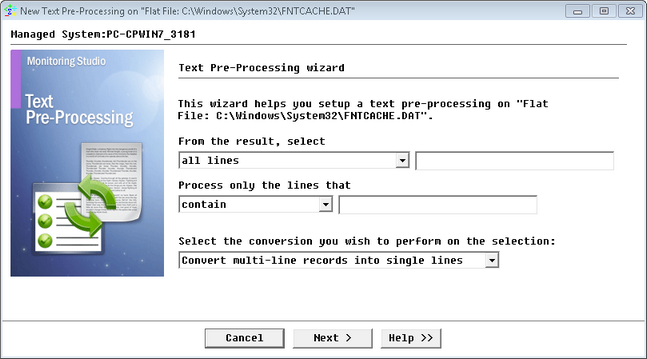
Text Pre-Processing Wizard — Welcome Page
| 2. | (Optional) If you need to filter the Monitor output to remove unwanted text before parsing it, select which lines of the result should be scanned: |
| ▪ | all lines/only the following line numbers: Specify whether all the lines of the result should be processed or enter the list of line numbers you wish to process separated by a semi-colon (;). Lines are specified as follows: |
x, y: line x and line y
x-y: all lines from x to y inclusive
x: Only line x
x-: all lines from x to the end of the file inclusive
| ▪ | contain/do not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be contained in the selected lines. |
| 3. | Select Convert multi-line records into single line and click Next. |
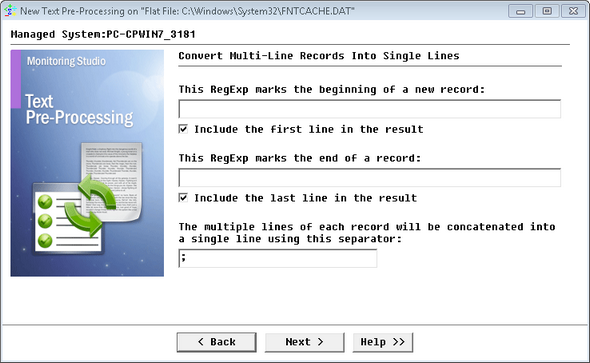
Text Pre-Processing Wizard: Convert multi-line records into single lines — Start/End of line definition
| 4. | Define the first and/or last lines of the paragraphs: |
| ▪ | This RegExp marks the beginning of a new record: Enter the regular expression or string that marks the beginning of a new record. Please note that the regular expression can match with any part of the first line of each paragraph. If needed, include the first line in the result. |
| ▪ | This RegExp marks the end of a record: Enter the regular expression or string that marks the end of a new record. Please note that the regular expression can match with any part of the first line of each paragraph. If needed, include the last line in the result. |
The entire line containing the specified RegExp will be returned.
|  The regular expression ^$ can be used to match an empty line. The regular expression ^$ can be used to match an empty line. |
 You can specify a regular expression that only identifies the beginning of a new paragraph (record). In this case, Monitoring Studio skips the content until it finds a line matching with the specified criteria. The text that follows this line (and optionally including this first line) is concatenated in a single line by using the specified separator, until Monitoring Studio finds another line that matches with the specified regular expression. Each line in the original content that matches with this regular expression produces a new line in the result content. The same is true for the regular expression that marks the end of a paragraph (or record). You can specify a regular expression that only identifies the beginning of a new paragraph (record). In this case, Monitoring Studio skips the content until it finds a line matching with the specified criteria. The text that follows this line (and optionally including this first line) is concatenated in a single line by using the specified separator, until Monitoring Studio finds another line that matches with the specified regular expression. Each line in the original content that matches with this regular expression produces a new line in the result content. The same is true for the regular expression that marks the end of a paragraph (or record).
 If you specify both regular expressions to identify the beginning and the end of a record, Monitoring Studio will only take into account the text content that is in the between lines that matches these regular expressions (i.e. between the start line and the end line). Lines in the original text between a line matching the end marker and the next line matching the beginning marker will be skipped and not integrated in the text result. If you specify both regular expressions to identify the beginning and the end of a record, Monitoring Studio will only take into account the text content that is in the between lines that matches these regular expressions (i.e. between the start line and the end line). Lines in the original text between a line matching the end marker and the next line matching the beginning marker will be skipped and not integrated in the text result.
| ▪ | Specify the character to be used as a separator. |
| 7. | Click Finish. The output will be displayed at the next discovery by the TransformResult parameter. |
You can now perform string searches, extract numeric values, map values or build dynamic objects from the TransformResult parameter output.
To convert XML to CSV
| 1. | In the PATROL Console, right-click the Monitor instance (File, Command Line, Web Request, etc.) and select KM Commands > New > Text Preprocessing... |
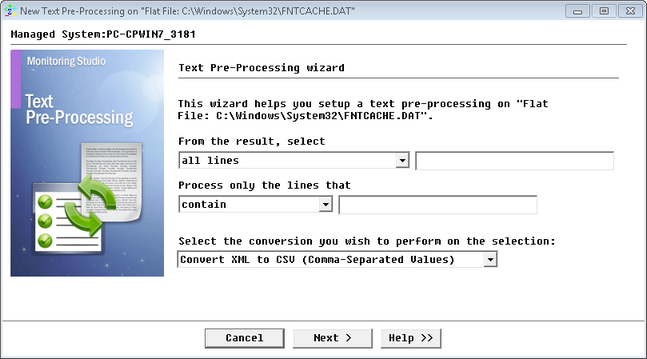
Text Pre-Processing Wizard — Welcome Page
| 2. | (Optional) If you need to filter the Monitor output to remove unwanted text before parsing it, select which lines of the result should be scanned: |
| ▪ | all lines/only the following line numbers: Specify whether all the lines of the result should be processed or enter the list of line numbers you wish to process separated by a semi-colon (;). Lines are specified as follows: |
x, y: line x and line y
x-y: all lines from x to y inclusive
x: Only line x
x-: all lines from x to the end of the file inclusive
| ▪ | contain/do not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be contained in the selected lines. |
| 3. | Select Convert XML to CSV (Comma-Separated Values) and click Next. |
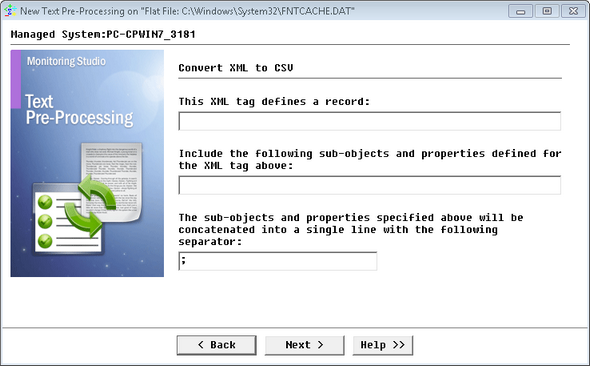
Text Pre-Processing Wizard: Convert XML to CSV — Object Definition
| 4. | Enter the XML tag that defines the record, sub-objects, and properties, the character to be used as a separator and click Next. |
| 6. | Click Finish. The output will be displayed at the next discovery by the TransformResult parameter. |
You can now perform string searches, extract numeric values, map values or build dynamic objects from the TransformResult parameter output.
To convert JSON to CSV
| 1. | In the PATROL Console, right-click the Monitor instance (File, Command Line, Web Request, etc.) and select KM Commands > New > Text Preprocessing... |
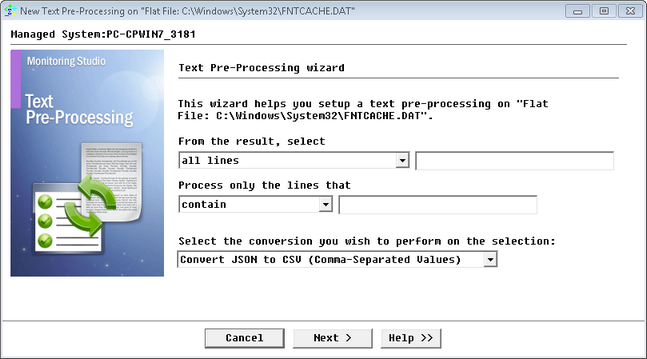
Text Pre-Processing Wizard — Welcome Page
| 2. | (Optional) If you need to filter the Monitor output to remove unwanted text before parsing it, select which lines of the result should be scanned: |
| ▪ | all lines/only the following line numbers: Specify whether all the lines of the result should be processed or enter the list of line numbers you wish to process separated by a semi-colon (;). Lines are specified as follows: |
x, y: line x and line y
x-y: all lines from x to y inclusive
x: Only line x
x-: all lines from x to the end of the file inclusive
| ▪ | contain/do not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be contained in the selected lines. |
| 3. | Select Convert JSON to CSV (Comma-Separated Values) and click Next. |

Text Pre-Processing Wizard: Convert JSON to CSV — JSON Entry Key Definition
| 4. | Enter the JSON entry key that defines the record, a list of properties (delimited by a semi-colon) and click Next. |
| 5. | List the properties defined for the provided JSON entry. Separate each property with a semi-colon (;). |
| 6. | Specify which separator to use to isolate each property in the output file, such as dot (.), dash (-), double semi-colon (;;), comma (,), pipe (|), plus sign (+), etc. |
| 8. | Click Finish. The output will be displayed at the next discovery by the TransformResult parameter. |
You can now perform string searches, extract numeric values, map values or build dynamic objects from the TransformResult parameter output.
To convert JSON to Flat Map
| 1. | In the PATROL Console, right-click the Monitor instance (File, Command Line, Web Request, etc.) and select KM Commands > New > Text Preprocessing... |

Text Pre-Processing Wizard — Welcome Page
| 2. | (Optional) If you need to filter the Monitor output to remove unwanted text before parsing it, select which lines of the result should be scanned: |
| ▪ | all lines/only the following line numbers: Specify whether all the lines of the result should be processed or enter the list of line numbers you wish to process separated by a semi-colon (;). Lines are specified as follows: |
x, y: line x and line y
x-y: all lines from x to y inclusive
x: Only line x
x-: all lines from x to the end of the file inclusive
| ▪ | contain/do not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be contained in the selected lines. |
| 3. | Select Convert JSON to Flat Map (Property=Value Pairs) and click Next. |

Text Pre-Processing Wizard: Convert JSON to Flat Map — Extraction Confirmation
| 6. | Click Finish. The output will be displayed at the next discovery by the TransformResult parameter. |
You can now perform string searches, extract numeric values, map values or build dynamic objects from the TransformResult parameter output.
To extract text from HTML
| 1. | In the PATROL Console, right-click the Monitor instance (File, Command Line, Web Request, etc.) and select KM Commands > New > Text Preprocessing... |
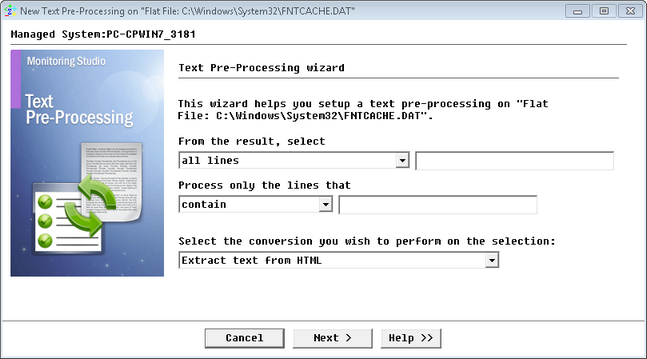
Text Pre-Processing Wizard — Welcome Page
| 2. | (Optional) If you need to filter the Monitor output to remove unwanted text before parsing it, select which lines of the result should be scanned: |
| ▪ | all lines/only the following line numbers: Specify whether all the lines of the result should be processed or enter the list of line numbers you wish to process separated by a semi-colon (;). Lines are specified as follows: |
x, y: line x and line y
x-y: all lines from x to y inclusive
x: Only line x
x-: all lines from x to the end of the file inclusive
| ▪ | contain/do not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be contained in the selected lines. |
| 3. | Select Extract text from HTML (Comma-Separated Values) and click Next. |
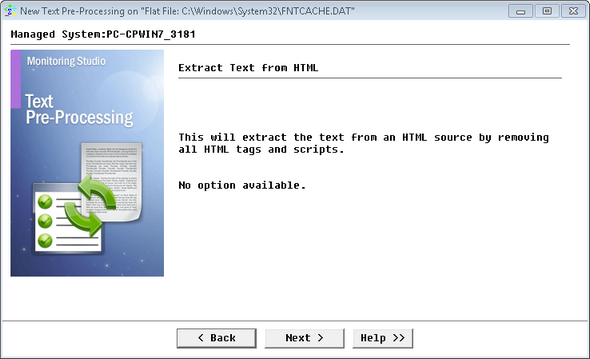
Text Pre-Processing Wizard: Extract text from HTML — Extraction Confirmation
| 6. | Click Finish. The output will be displayed at the next discovery by the TransformResult parameter. |
You can now perform string searches, extract numeric values, map values or build dynamic objects from the TransformResult parameter output.
To process text through an external command
This option should be selected if text inputs (files, output of commands, Web requests, etc.) need to be transformed in a special way in order to be parsed with Monitoring Studio’s String Searches and Numeric Value Extractions. If the built-in text transformation features of Monitoring Studio cannot handle such "specially formatted" text, you will have to process the content through a custom script or utility that performs the required transformation. The main advantage of processing the text through an external command feature is that it enables you to customize the processing of almost any source of information important to your technology.
| 1. | In the PATROL Console, right-click the Monitor instance (File, Command Line, Web Request, etc.) and select KM Commands > New > Text Preprocessing... |

Text Pre-Processing Wizard — Welcome Page
| 2. | (Optional) If you need to filter the Monitor output to remove unwanted text before parsing it, select which lines of the result should be scanned: |
| ▪ | all lines/only the following line numbers: Specify whether all the lines of the result should be processed or enter the list of line numbers you wish to process separated by a semi-colon (;). Lines are specified as follows: |
x, y: line x and line y
x-y: all lines from x to y inclusive
x: Only line x
x-: all lines from x to the end of the file inclusive
| ▪ | contain/do not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be contained in the selected lines. |
| 3. | Select Text processing through an external command and click Next. |
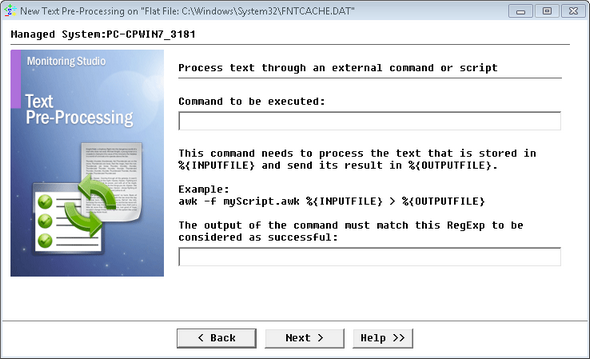
Text Pre-Processing Wizard: Text processing through an external command — Command Definition
| 4. | Specify the command to be executed to transform the text: |
| ▪ | Command to be executed: Enter the command to be executed on the localhost where your PATROL Agent is installed. The principle is very similar to the "pipe" mechanism of the UNIX shell except that the content is not passed directly but is stored in a temporary file and then the result needs to be stored in another temporary file. Hence the command line you specify needs to take the %{INPUTFILE} macro as an argument (the %{INPUTFILE} macro is replaced by the real temporary input file location at run time) as well as %{OUTPUTFILE}. |
 This command is executed on the host where the PATROL Agent is installed, not on the target Host. This command is executed on the host where the PATROL Agent is installed, not on the target Host.
| ▪ | The output of the command must match this RegExp to be considered as successful: Enter a RegExp to avoid typical path problems such as getting "... not found" error messages instead of the properly transformed text |
 If your command line redirects its output to %{OUTPUTFILE}, the validation regular expression is likely to fail because the standard output is empty and thus matches with nothing. Use a validation regular expression only if your command line is able to produce both the %{OUTPUTFILE} and some text to its standard output. If your command line redirects its output to %{OUTPUTFILE}, the validation regular expression is likely to fail because the standard output is empty and thus matches with nothing. Use a validation regular expression only if your command line is able to produce both the %{OUTPUTFILE} and some text to its standard output.
 Command lines are executed locally, therefore it is not possible to use the awk command when monitoring a UNIX/Linux system from Windows. Command lines are executed locally, therefore it is not possible to use the awk command when monitoring a UNIX/Linux system from Windows.
 Macros are case sensitive and should then always be written in uppercase. Macros are case sensitive and should then always be written in uppercase.
| 6. | Click Finish. The output will be displayed at the next discovery by the TransformResult parameter. |
You can now perform string searches, extract numeric values, map values or build dynamic objects from the TransformResult parameter output.
|