|
The Windows Event Monitor tracks events posted by your technology to consolidate the monitoring under a single icon and avoid you to look up in the Windows Event Log. It also enables you to define automatic acknowledgment of previously triggered alerts by specifying the Windows event that will acknowledge the alert.
 Windows events on Windows 2003 systems can only be monitored locally. Windows events on Windows 2003 systems can only be monitored locally.
To monitor a Windows event log
| 1. | In the PATROL Console, right-click the Host or Monitor Group icon and select KM Commands > New > Monitor... |
| 2. | Select Windows Event from the drop-down list and click Next to retrieve all the available Windows event logs from your local or remote system. |
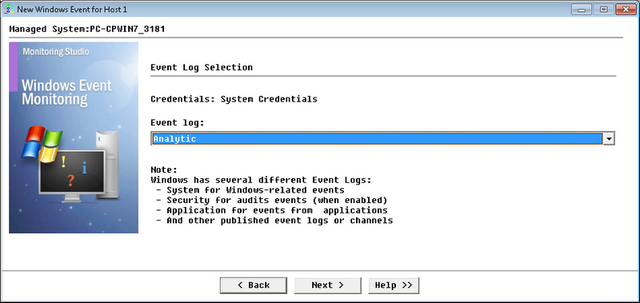
Monitoring Windows Events — Welcome Page
| 3. | Select the Windows event log that you want to monitor from the Event log drop-down menu and click Next. |
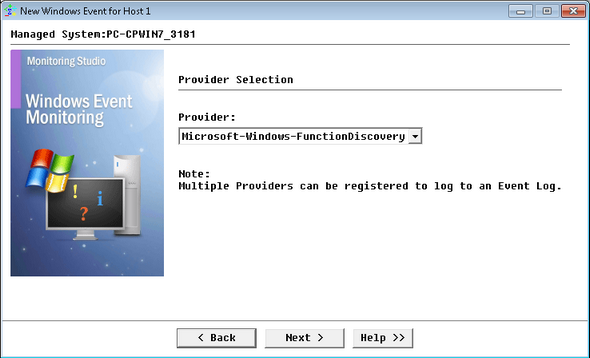
Monitoring Windows Events — Provider Selection
| 4. | All available providers are listed in the Provider drop-down menu. Select one from the list and click Next. |
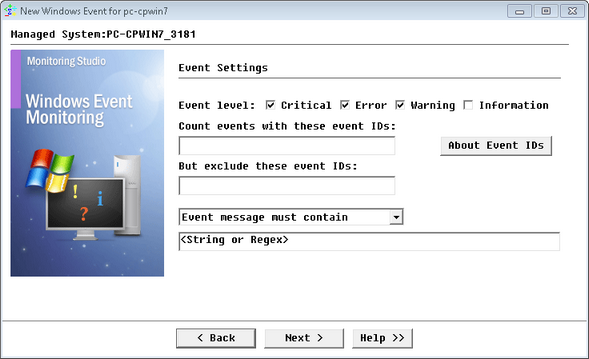
Monitoring Windows Events — Event Settings
| 5. | (Optional) Define the Event Settings: |
| ▪ | Event level: Select the event level(s) to monitor (Critical, Error, Warning, Information) |
| ▪ | Count events with these events IDs: Enter the ID(s) of the event(s) to be considered for alerting. |
| ▪ | But exclude these event IDs: Enter the ID(s) of the event(s) to be excluded from alerting. |
| ▪ | Event message must contain/must not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be found in the event message. |
| ▪ | About Event IDs: Click this button to get further details on the event ID syntax. |
 Use a comma (,) to separate several IDs or a hyphen (-) between start and end values to indicate a range (Example: 4372,4375,4380-4385). Use a comma (,) to separate several IDs or a hyphen (-) between start and end values to indicate a range (Example: 4372,4375,4380-4385).
 If you are unsure about the characteristics of the Windows event you want to detect, you may use the Monitoring Studio built-in Windows Event Log Reader tool to view content of the event Logs and the characteristics of the events. Right-click a Host icon > KM commands > Tools > Windows Event Log Reader. If you are unsure about the characteristics of the Windows event you want to detect, you may use the Monitoring Studio built-in Windows Event Log Reader tool to view content of the event Logs and the characteristics of the events. Right-click a Host icon > KM commands > Tools > Windows Event Log Reader.
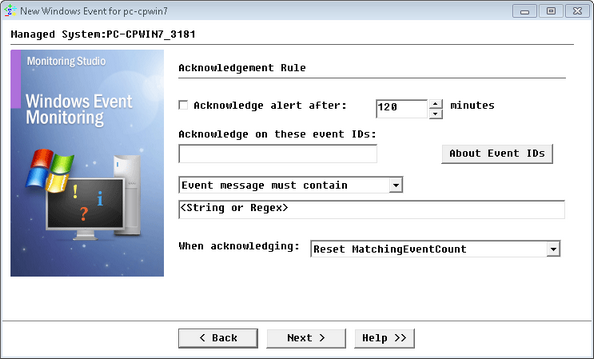
Monitoring Windows Events — Acknowledgment Rule
| 7. | (Optional) Define the Acknowledgment Rule: |
| ▪ | Acknowledge alert after: Check this option and then specify the time in minutes after which the alerts will be acknowledged (Default: 120 minutes). |
| ▪ | Acknowledge on these events IDs: Enter the ID(s) of the event(s) that you wish to acknowledge on. Use a comma (,) to separate several IDs or a hyphen (-) between start and end values to indicate a range. |
| ▪ | Event message must contain/must not contain: Enter the string or regular expression to look for, and specify whether or not it should be found in the event message. |
| ▪ | When acknowledging: Choose between resetting the MatchingEventCount parameter, i.e. clear all previous alerts or simply decreasing it by one; i.e. clear the previous alert. |
| 10. | Click Finish. The corresponding Windows Event Log instance (Windows Event Log: <Display Name>) is created in the PATROL Console. The collected parameters for Windows Event Log instances are listed in the SEN_MS_WINEVENT chapter. |
Configuring the Windows Event Cache Refreshing Frequency
Monitoring Studio relies on a cache mechanism to share the information among the Monitors in order to use as little resources as possible on the target Host and over the network. The cache will be refreshed if one of the Monitors needs to collect data (polling interval reached) and the cache is older than the selected minimum cache refresh frequency.
All Windows event data on the selected host are cached and shared by all Windows Event Monitors defined for this host. By default, the Windows event cache is refreshed minimum every 15 seconds. It is however possible to change this minimum cache refresh interval as described in the Setting the Polling Interval section.
|